In the vast landscape of mental health, the interplay between nutrition and mood is often overlooked. While we frequently hear about the roles of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and magnesium in mental health, one vital nutrient that doesn’t get as much attention is biotin, also known as vitamin B7. Often celebrated for its role in skin, hair, and nail health, biotin also plays a crucial, albeit lesser-known, role in brain function and mental well-being. Recent research suggests that adequate biotin intake could be a key factor in depression prevention.
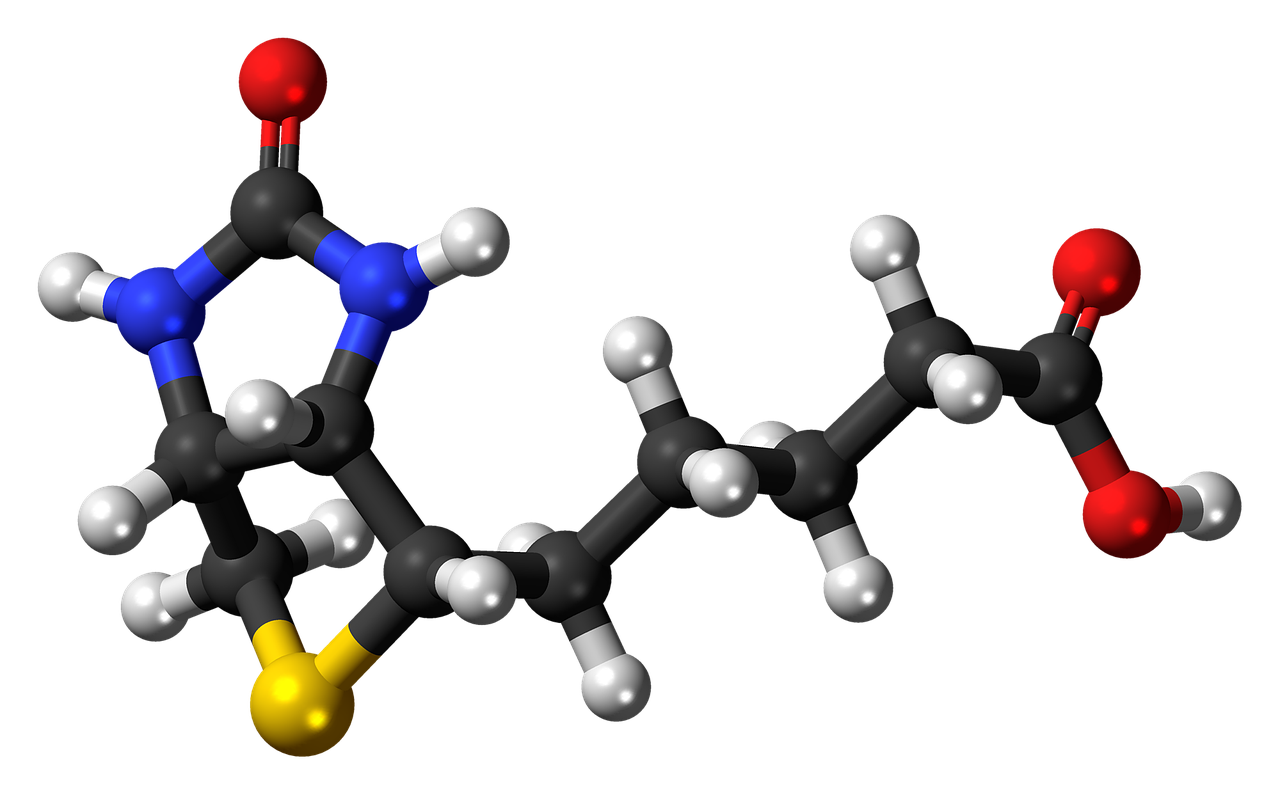
Understanding Biotin’s Role in the Body
Biotin is a water-soluble B-vitamin that acts as a coenzyme in the body, meaning it helps enzymes perform their functions. It is involved in a variety of metabolic processes, including the breakdown of fats, carbohydrates, and proteins into energy. This energy production is not only vital for physical health but also for maintaining optimal brain function.
Biotin is also essential for the synthesis of fatty acids, which are critical components of brain cell membranes. Without sufficient biotin, the body’s ability to produce energy and maintain cellular integrity, particularly in the brain, could be compromised, potentially leading to neurological and psychological symptoms.
The Link Between Biotin and Depression
Emerging research suggests that there may be a link between biotin deficiency and the development of depressive symptoms. This connection is thought to be due to biotin’s role in synthesizing neurotransmitters, the brain chemicals responsible for mood regulation.
For example, biotin is involved in the metabolism of amino acids like tryptophan, which is a precursor to serotonin, often dubbed the “feel-good” neurotransmitter. Low serotonin levels have been strongly associated with depression. By ensuring adequate biotin levels, the body can more effectively produce serotonin, thereby potentially reducing the risk of depression.
Furthermore, biotin deficiency can lead to symptoms like fatigue, irritability, and cognitive difficulties, all of which can exacerbate or mimic the symptoms of depression. In severe cases, biotin deficiency can lead to neurological issues such as seizures, which further highlights the importance of this nutrient in maintaining mental health.

Who is at Risk of Biotin Deficiency?
Although biotin deficiency is considered rare in healthy individuals, certain populations are more susceptible. These include:
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women: Increased biotin demands during pregnancy and lactation can lead to marginal deficiencies.
- Individuals with certain genetic disorders: Some genetic conditions affect biotin metabolism or absorption.
- People with gastrointestinal disorders: Conditions like Crohn’s disease or those who have undergone gastrointestinal surgeries may have impaired absorption of biotin.
- Chronic alcohol users: Alcohol can interfere with the absorption and metabolism of biotin.
- Those on long-term antibiotic therapy: Antibiotics can alter gut flora, which plays a role in biotin synthesis.


Ensuring Adequate Biotin Intake
To maintain optimal biotin levels and potentially safeguard against depression, it’s essential to consume a balanced diet rich in biotin-containing foods. Some excellent sources of biotin include:
- Egg yolks
- Nuts and seeds
- Legumes
- Whole grains
- Organ meats like liver and kidney
- Certain vegetables like sweet potatoes, spinach, and broccoli
For individuals at risk of deficiency or those looking to optimize their mental health, a biotin supplement may also be beneficial. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.


Integrating Biotin into a Holistic Approach to Mental Health
While biotin alone is not a cure for depression, it is an essential piece of the puzzle in maintaining mental health. A holistic approach to mental well-being should always include attention to diet and nutrient intake. Understanding and addressing potential biotin deficiencies, alongside other lifestyle and therapeutic interventions, can better support our mental health and overall quality of life.
Ensuring you get enough biotin may be a simple, yet effective, step in preventing depression and promoting emotional balance. Whether through diet or supplementation, this often-overlooked nutrient could play a more significant role in mental health than we’ve ever imagined.

Sahebkar, A., Beccuti, G., Simental-Mendia, L. E., Nobili, V., & Bo, S. (2016). Nigella sativa (black seed) effects on plasma lipid concentrations in humans: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Pharmacological research, 106, 37-50.

Schedule a Call

To Find Out if Your Depression may be Rooted in Nutrient Deficiency
Let’s Heal Together!


Phone
253.507.5775
Admin@NeoGenesisNutrition.com
Address
2607 Bridgeport Way W Ste. 2M University Place, WA 98466
Disclaimer: The content of this blog is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional before making any changes to your diet, lifestyle, or treatment plan.

